Gestational diabetes is a condition that occurs during pregnancy and affects how your body processes glucose. While many women with gestational diabetes might not experience any symptoms at all, some may notice certain signs that could indicate the presence of this condition. In this article, we will delve into the various symptoms of gestational diabetes and explore how they can impact pregnant individuals.
What is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes is a form of diabetes that develops specifically during pregnancy. It occurs when the body is unable to produce enough insulin to meet the increased demand during this period. This can result in elevated blood sugar levels, which, if left unmanaged, can lead to various health complications for both the mother and the baby.
Common Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes
- Frequent Urination: One of the hallmark symptoms of gestational diabetes is increased urination. The high blood sugar levels prompt the kidneys to work overtime, causing frequent trips to the bathroom.
- Excessive Thirst and Dry Mouth: Elevated blood sugar levels can lead to dehydration, which triggers an increased sense of thirst and a dry mouth.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Pregnant individuals with gestational diabetes might experience persistent fatigue and weakness due to the body’s inability to effectively utilize glucose for energy.
- Blurred Vision: Fluctuations in blood sugar levels can temporarily affect vision, leading to blurred vision in some cases.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some women may experience nausea and vomiting, which can be exacerbated by the changes in blood sugar levels.
Uncommon Symptoms to Watch For
While the symptoms mentioned above are more common, there are other, less frequently observed signs that might indicate gestational diabetes.
- Persistent Yeast Infections: High blood sugar levels can create an environment conducive to yeast growth, leading to recurrent yeast infections.
- Increased Hunger: Insulin resistance can trigger feelings of increased hunger, even shortly after a meal.
Managing Gestational Diabetes Symptoms
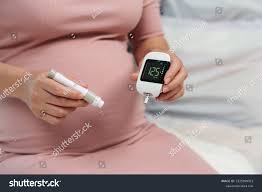
If you suspect that you might be experiencing symptoms of gestational diabetes, it’s crucial to seek medical advice promptly. Early detection and management can significantly reduce the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby. Your healthcare provider may recommend blood sugar monitoring, dietary changes, regular physical activity, and, in some cases, insulin therapy to ensure that blood sugar levels are well controlled.
In conclusion, gestational diabetes symptoms can vary from person to person, and not all pregnant individuals will experience them. However, it’s important to pay attention to any changes in your body during pregnancy and to communicate with your healthcare provider about any concerns. By actively managing gestational diabetes and working closely with your medical team, you can ensure the best possible outcome for both you and your baby.






Leave a Reply